A ScaleArc Kerberized Cluster relies on Kerberos Authentication for cluster user authentication.
The main reason for using Kerberos is that NTLM user authentication requires the original username and password as well as a direct connection/communication with the originating machine requesting authentication.
Kerberos has a major advantage since it uses session-specific keys. Using Kerberos, the original password is only authenticated by either the Active Directory Controller (ADC) or the Backup Domain Controller (BDC) when the user first logs on to the Kerberos realm (AD domain). Once the authentication is successful, the session-specific keys provided by the authenticating server earlier can authenticate any other services for the host/application.
Review the sections below for the detailed steps to be executed when setting a Kerberized ScaleArc cluster:
- Configure a hostname and VIP
- Configure Windows AD for delegation
- Create a cluster
- Verify Kerberos Authentication Offload
Configure a hostname and VIP
Kerberos authentication uses hostnames to identify machines and services in the domain. This requires a valid and unique hostname for the VIP (Virtual IP address) on the ScaleArc machine.
Create a hostname (DNS setup)
Follow these steps:
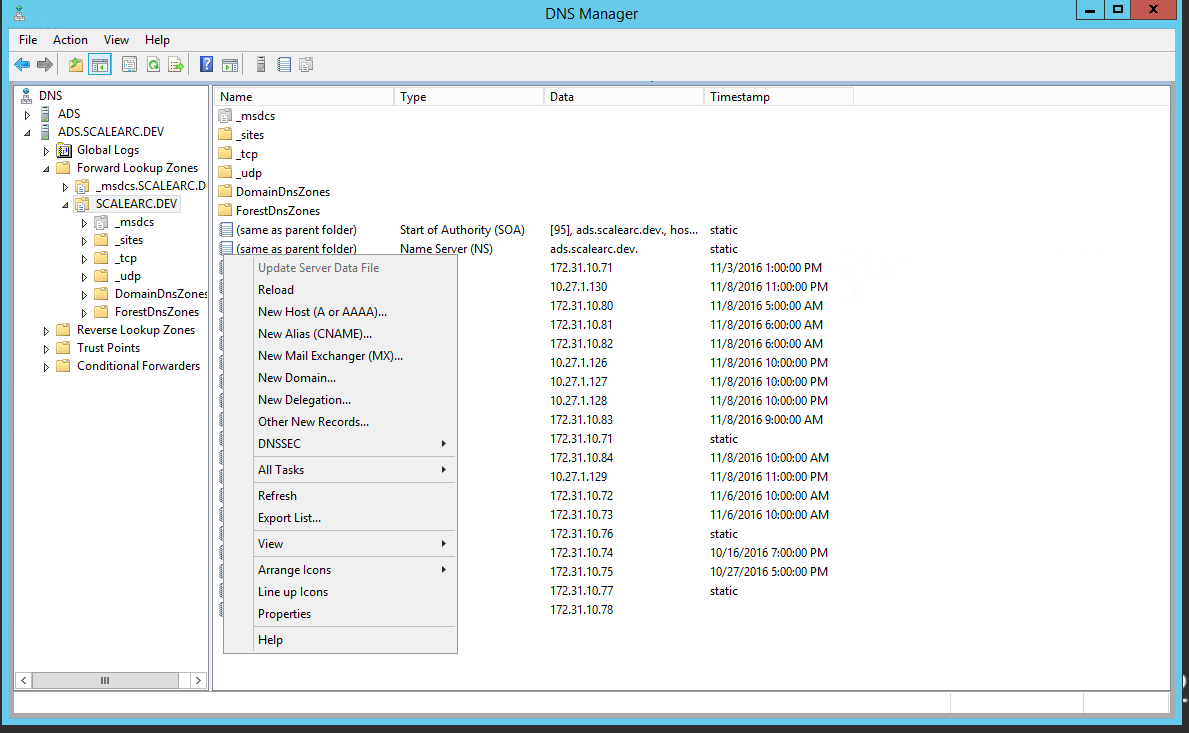
- Open DNS manager on the AD server.
- Navigate to the domain name, and right-click it.
- Select New Host from the drop-down menu.
-
Enter a new hostname; for example, scale-test. The FQDN for the record appears in the field.
Important Make sure you enter a hostname that does not include special characters such as underscore or period.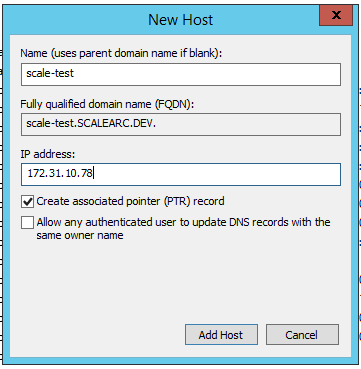
- Next, enter the IP address associated with the hostname.
- Select "Create associated pointer (PTR) record". This creates a reverse name lookup record for the host.
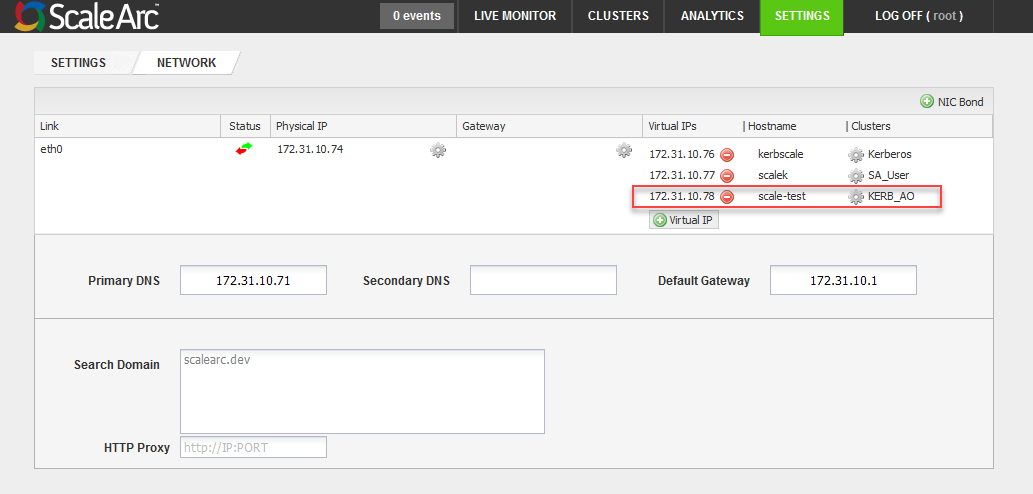
- Click Add Host. At this time you should have both the forward and reverse lookup for the virtual IP (VIP) set to hostname scale-test.
Configure VIP for Kerberos
This example configures a VIP for the Kerberized cluster.
Follow these steps:
- Click the SETTINGS tab > Network Settings on the ScaleArc dashboard.
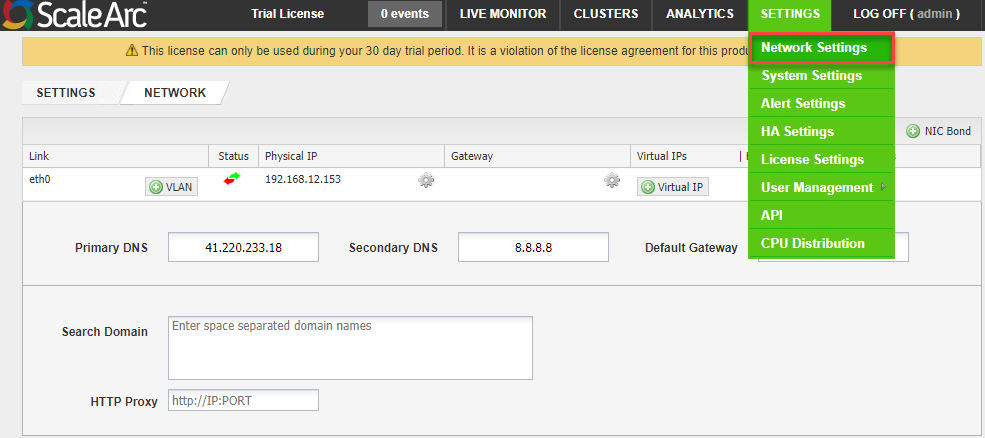
- Click Virtual IP.
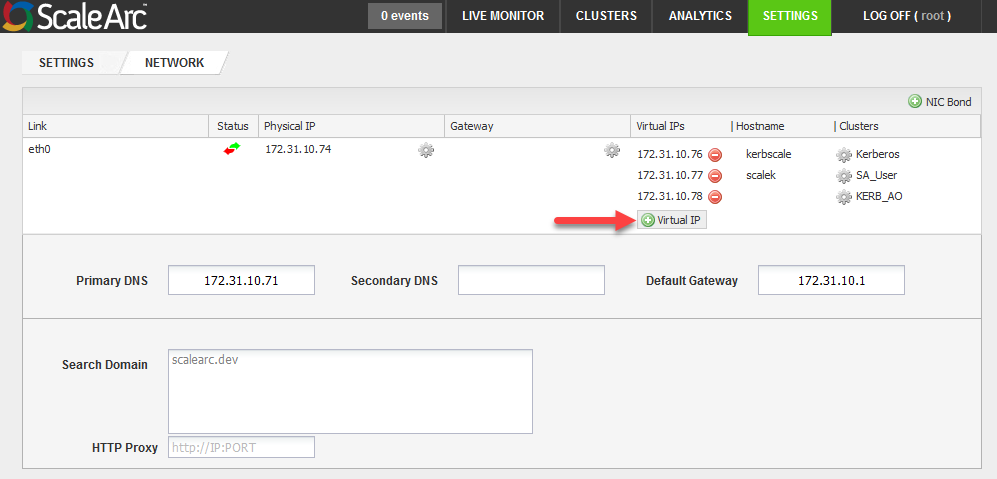
- Select a subnet mask.
- Enter the hostname that you created.

- Click Save.
- The address now appears on the screen.
Configure Windows AD for delegation
ScaleArc supports constrained delegation in which a user's identity and credentials are passed along to explicitly specified servers or services.
Prerequisites
To configure ScaleArc to use constrained delegation, make sure you have the following:
- Set the NTP server in ScaleArc to the one set on the Active Directory server of the Key Distribution Center (KDC). It is advisable to set maximum tolerance for computer clock synchronization to a value of five minutes.
- You have domain administrator account privileges.
- Ensure that forward and reverse DNS lookup zones are configured correctly for SQL server and ScaleArc (all virtual IPs).
-
Check the DNS server, it should be the same as the one configured in Active Directory or the authentication server in the Kerberos environment (KDC). Note that ScaleArc's hostname should be in lower case without any special characters, such as underscore or period.
Join ScaleArc as a machine account
Follow these steps to join ScaleArc as a machine account:
- Click the SETTINGS tab > System Settings on the ScaleArc dashboard.
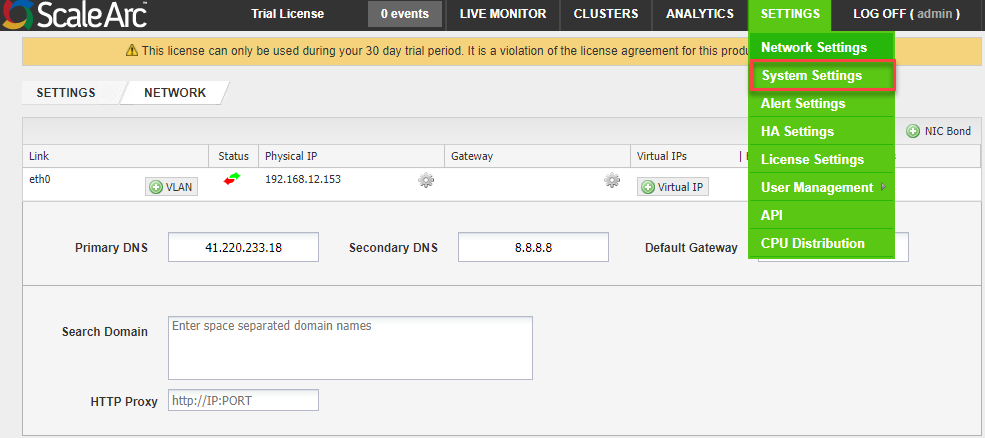
- Click on the AD Integration tab.
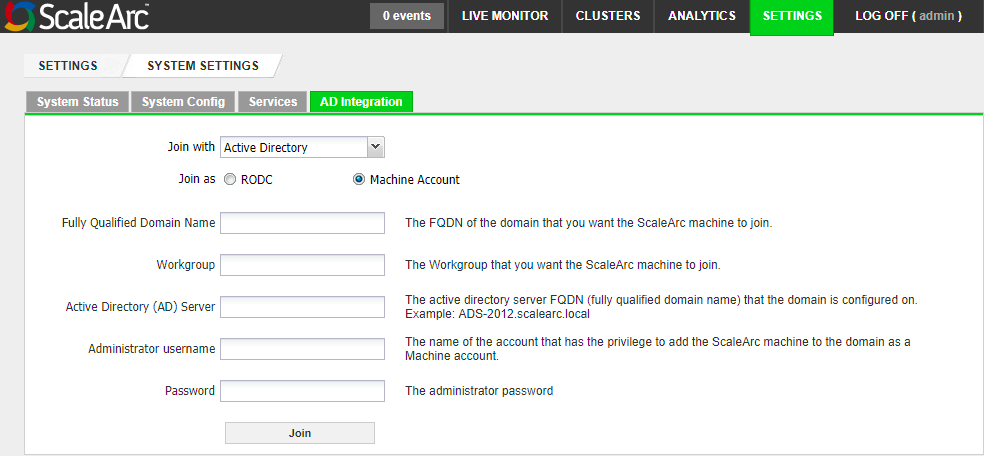
-
Select Machine Account. Then, complete the fields as follows:
Field Description Default/User input Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) The FQDN of the domain that you want the ScaleArc appliance to join.
Enter an appropriate domain name. Workgroup The workgroup (Domain Netbios Name) that you want the ScaleArc appliance to join.
Enter a valid workgroup name. Active Directory (AD) Server
The active directory server FQDN (fully qualified domain name) that the domain is configured on. Note that the server name should not include a trailing dot (".") at the end, unless you are using a valid DNS entry for the name. Enter the FQDN. Administrator username The username of the account that has the privilege to add the ScaleArc appliance to the domain as a machine account.
Enter the username. Password The administrator password.
Enter the password. Advanced Settings The button to configure additional settings such as subdomains. This setting appears only after you join. Click to open the related screen. - Click Join to complete the setup. A successful join posts this dialog box. Click OK. Once connected, you can use Unjoin to leave the domain.
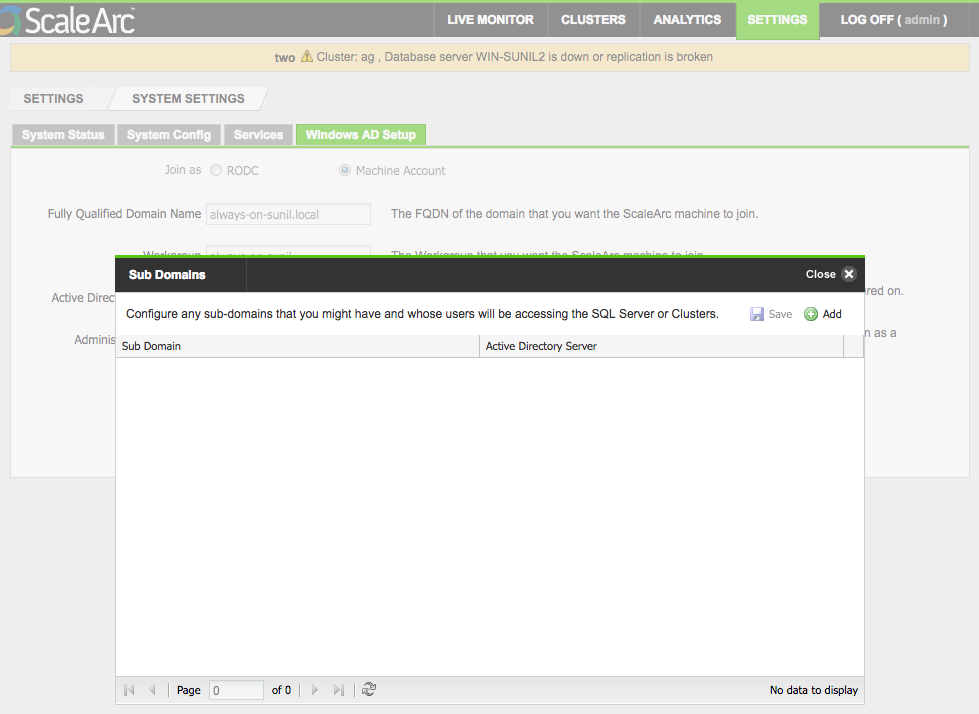
- Click Advanced Settings if you wish to add sub-domains.
- Enter one or more sub-domains and their corresponding AD servers. Click Add.
-
The ScaleArc appliance shows up in the Active Directory Users and Computers console. This creates a machine account for the ScaleArc appliance, using the naming convention <hostname$>.
Set up Service Principal Name (SPN) for ScaleArc
Next, set up SPN for ScaleArc. SPN is a unique identifier for a service on a network that uses Kerberos authentication. It consists of a service class, a hostname, and a port or the instance name. To create an SPN, use the SetSPN command-line utility.
Follow these steps to set up the Service Principal Name (SPN) for ScaleArc on AD from Windows PowerShell:
- Log in to the Active Directory server as a user with domain administrator privileges.
-
From PowerShell, set the Service Principal Name for ScaleArc on AD. Remember to specify the port correctly. In this example, the cluster listens on port 1433.
For a standalone server:
For AG (Availability Group) Listener:Syntax Setspn -A MSSQLSvc/<VIP_Hostname>.<domainname>:<port> <domain\ScaleArc hostname$> Example C:\>setspn -A MSSQLSvc/scale-test.krbs.com:1433 krbs\scale-pri$Syntax Setspn -A MSSQLSvc/<VIP_Hostname>.<domainname>:<port> <domain\ScaleArc hostname$> Example C:\>setspn -A MSSQLSvc/scale-test.krbs.com:1433 krbs\scale-pri$ Syntax for AG Listener Setspn -A MSSQLSvc/<AG LISTENER_Hostname>.<domainname>:<port><domain\domain admin user> Example C:\>setspn -A MSSQLSvc/aglsnr.krbs.com:1433 krbs\clsImportant: Larger AD infrastructures may delay the propagation of new SPN entries which could cause delays in those SPN entries being available for delegation. We recommend you wait up to an hour before continuing.If you are a cloud customer, instead of <VIP_Hostname> use the All IP hostname which was configured earlier.
Set up ScaleArc for delegation
- On the domain controller, access the Active Directory Users and Computers console.
- In the console tree, under Domain name, click Computers.
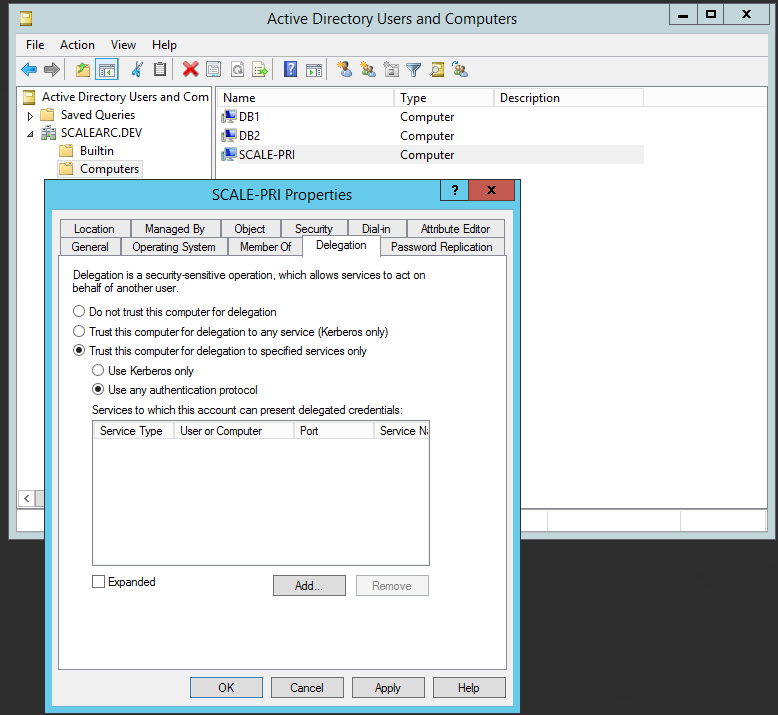
- Right-click the ScaleArc server, and then click Properties.
- On the Delegation tab, click Trust this computer for delegation to specified services only.
- Click Use any authentication protocol.
- Click Add, and then click to select Users and Computers.
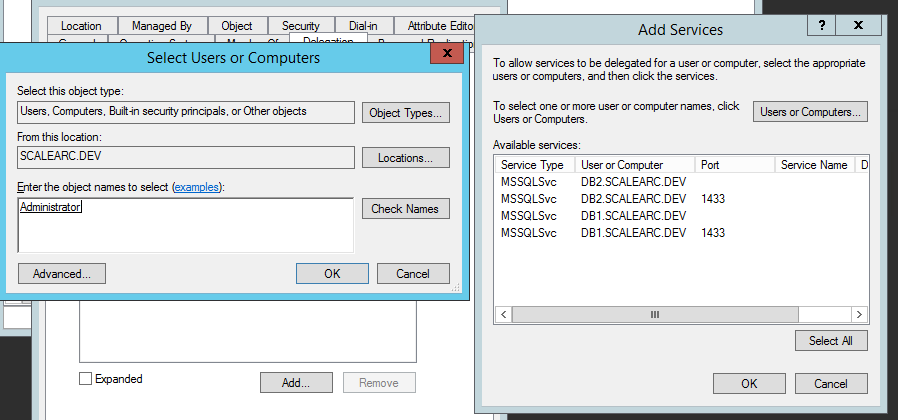
- Enter the domain user that has the necessary credentials to start and stop SQL services; then, click Select All and OK.
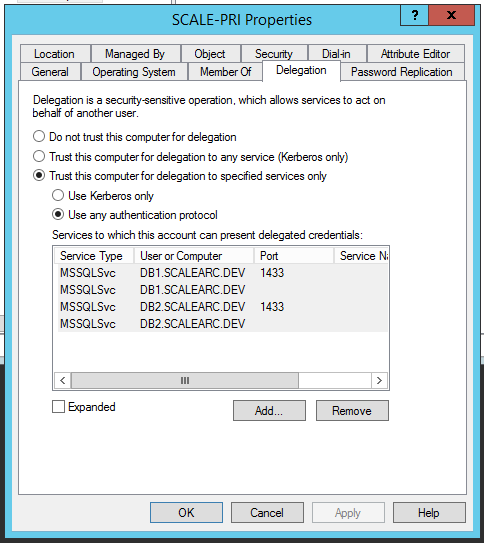
- From the Delegation tab, click Add. Then, click Users or Computers and enter the machine account name of the ScaleArc primary machine (for example, scale-pri$). Click Check Names and OK.
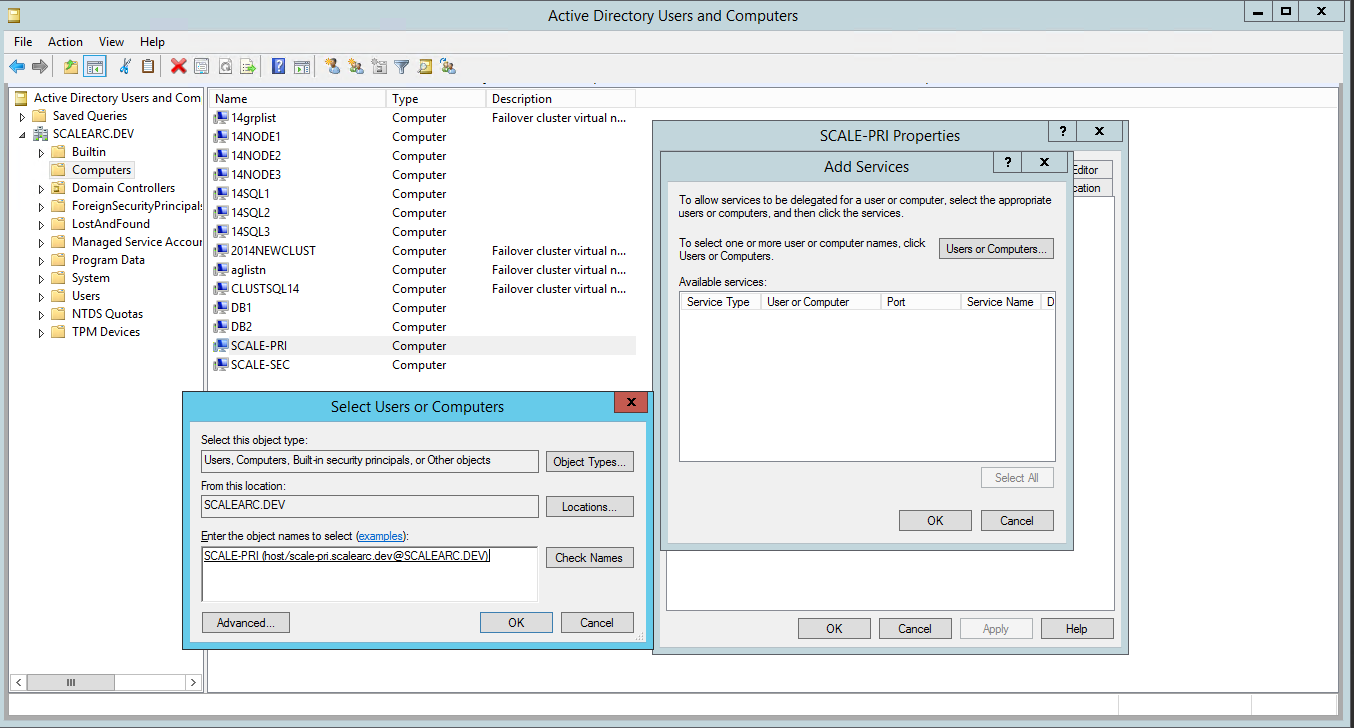
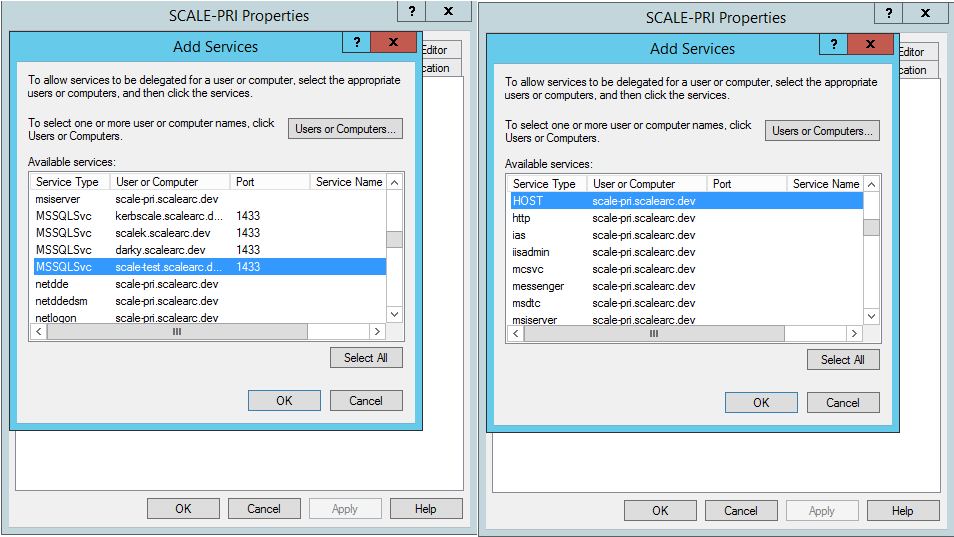
- Select the HOST and the MSSQLSvc service for the VIP created earlier. Press the Control key to select multiple entries. Click OK.
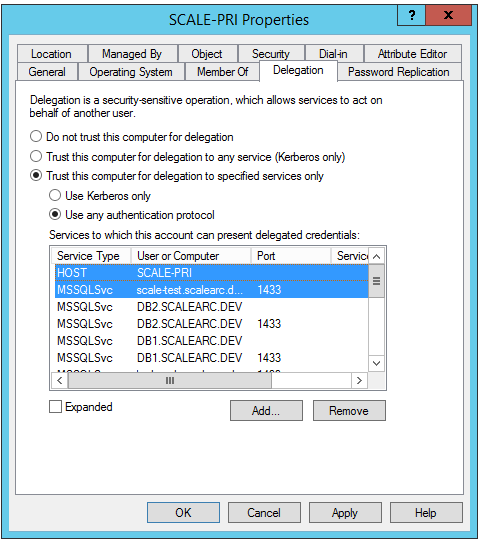
- The entries appear on the Delegation tab. Click OK.
Provide database access
This is a two-step process:
- Set up SQL Server for authentication with the ScaleArc's machine account
- Configure database access.
Grant access to ScaleArc's machine account
Follow these steps to grant minimum privileges to ScaleArc on SQL Server:
- From the machine running SQL Server, log in to SQL Server Management studio.
- Connect to the server.
- Log in.
-
Locate Security > Logins > New Login. Remember to add $ at the end of the login name.
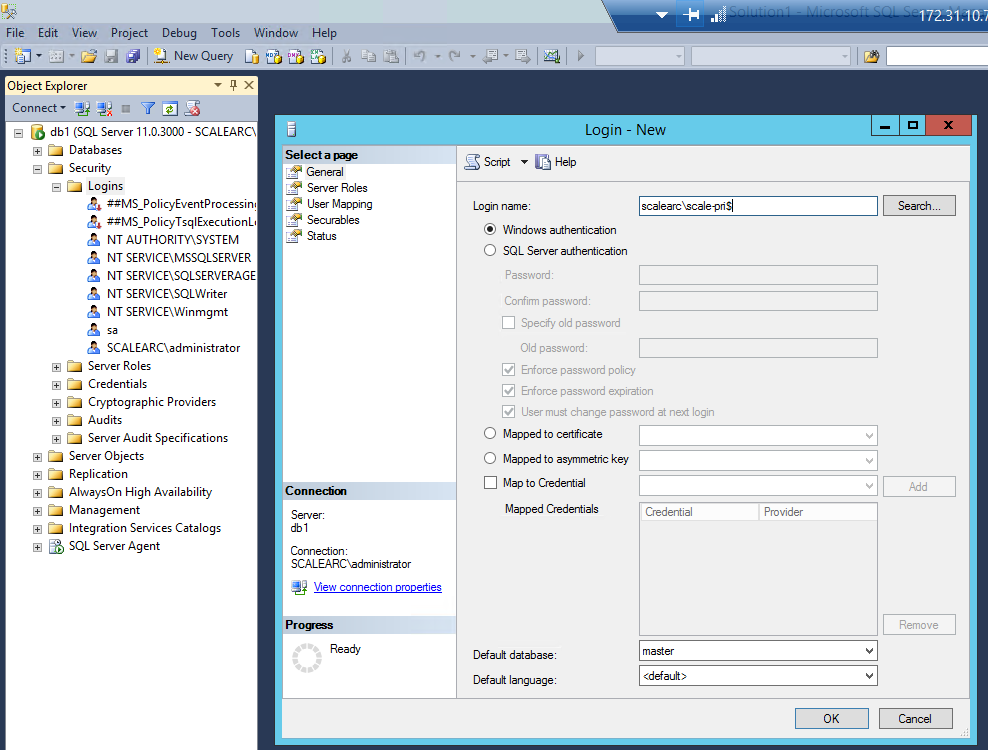
- Select the User. Right-click on properties.
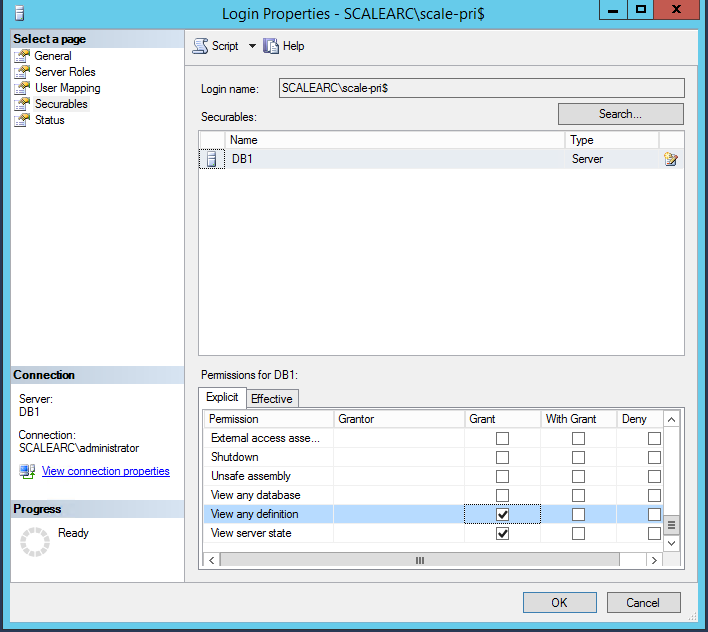
- Under the Explicit tab, select the following permissions.
- View Any Definition.
- View Server status.
- Click OK.
Create a cluster
You are now ready to create a Kerberized cluster in ScaleArc.
Define a cluster for Kerberos
Follow these steps:
- On the ScaleArc dashboard, click the CLUSTERS tab > Add Cluster button.
- Locate the Network section. This is the first panel on the Create Cluster screen.
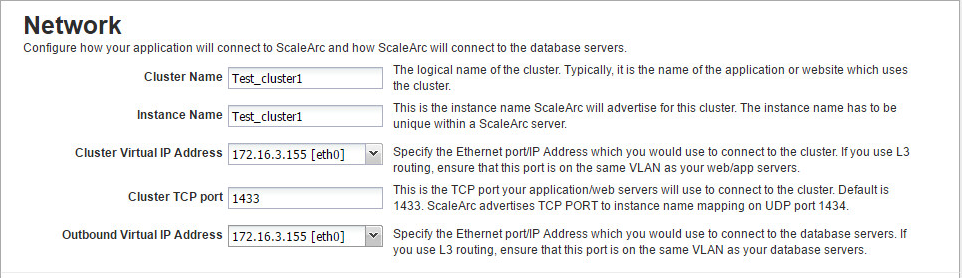
- Fill in the fields with valid information as outlined in Configuring ScaleArc endpoints.
-
Select the VIP address you created with the hostname for the field labeled Cluster Virtual IP Address.
If you are a cloud customer you can use All IP to set up the cluster.
Configure database access
Follow these steps:
- On the ScaleArc dashboard, click the CLUSTERS tab > Add Cluster button.
-
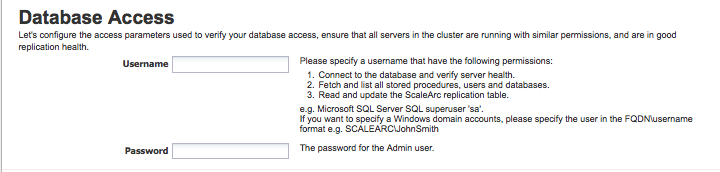
Locate and complete the Database Access section. This is the second panel on the Create Cluster screen.
-
If you have joined Windows AD as a machine account, the screen displays a pre-selected checkbox. If you de-select the checkbox, the cluster does not use Kerberos anymore for ScaleArc services and monitoring.
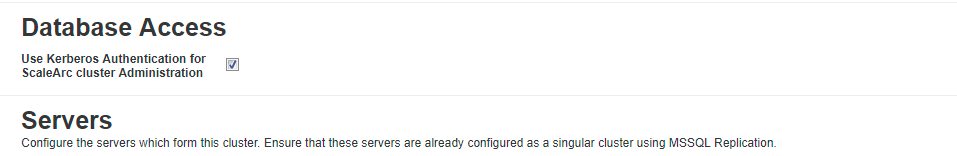 De-selecting the checkbox does not require you to unjoin the domain; nor does it have an impact on other clusters in the domain that have been configured for Kerberos authentication.
De-selecting the checkbox does not require you to unjoin the domain; nor does it have an impact on other clusters in the domain that have been configured for Kerberos authentication. - Next, configure database servers and SSL (optional) for the cluster.
- If you had selected the checkbox to Start Cluster after Setup (this is selected by default), the newly created cluster's green icon indicates that the cluster is running. If you had unchecked this option, the cluster icon will be red, indicating that you need to start the cluster. Click START in the Status column to run the cluster. The icon should turn green indicating it is now running. You can stop the cluster using the STOP button.
-
Verify ScaleArc Authentication Offload is ON.
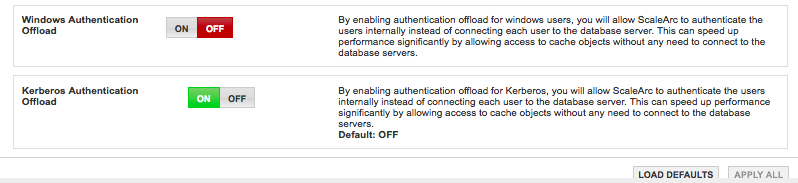
Verify Kerberos Authentication Offload
A fully-Kerberized cluster has the Kerberized Authentication Offload button set to ON when ScaleArc joins AD as a machine account. Click here to review ScaleArc settings for Kerberos.
- Navigate to CLUSTERS > Status column > Cluster Settings in the ScaleArc dashboard.
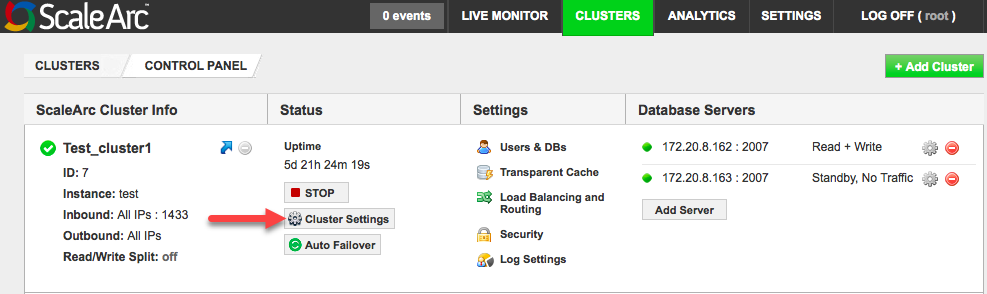
- Select the ScaleArc tab.
- Locate the Kerberos Authentication Offload button. Note that it is ON.