Overview
This article provides the steps to set up a local DNS using the hosts file (/etc/hosts) on the ScaleArc server for local domain name resolution. Having a local DNS will enable ScaleArc to connect to database servers using either their hostnames or the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) without having to rely on external DNS resolution that can be prone to network timeouts.
Prerequisites
- Environment: ScaleArc - all versions
- Access to the ScaleArc instance via SSH
- Root access to add entries to the
/etc/hostsfile. - If you have
idbuser permissions, you can edit the file with the sudo command:sudo vi /etc/hosts
Solution
DNS resolution issues may prevent ScaleArc from connecting to database servers thereby making the appliance unable to process traffic.
The /etc/hosts is an operating system file that is used by the DNS service to translate hostnames or domain names to IP addresses.
Follow these steps to configure the Local DNS to enable ScaleArc to connect to the database servers using either their hostnames or FQDN. As an example, we will be using the following domain, hostnames, and IP addresses. Change these to reflect your environment.
Domain: ignitetech.com DB Host 1: db01.ignitetech.com 192.168.12.215 DB Host 2: db02.ignitetech.com 192.168.12.150
- Open the
/etc/hostsfile using your editor of choice as follows-
$ sudo vi /etc/hosts
-
- Add the lines below to the end of the file as shown
-
192.168.12.215 db01.ignitetech.com db01
192.168.12.150 db02.ignitetech.com db02 - Include as many hosts as you have in your environment.
-
- Save the changes.
Testing
Using the ping command from the ScaleArc host, you should be able to ping any of the database servers using either their domain name or hostname as shown:
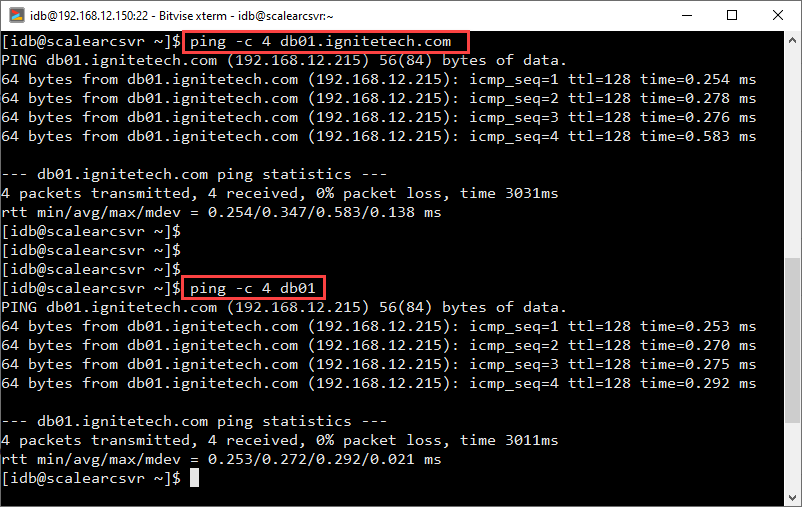
This confirms that ScaleArc will continue to operate and connect to the database servers without name resolution errors, regardless of whether the configuration is done using the hostname, domain name, or the IP address of the hosts.
pingcommand is preferred for testing the local name translation service. Other commands for testing DNS lookups such as the hostcommand or the nslookupcommand only query external DNS and overlook any configurations in /etc/hosts file.
Comments
0 comments
Article is closed for comments.